Why Are PVC Window and Door Profile Extrusion Machines Becoming So Popular?
In recent years, the demand for energy-saving and customized windows and doors has been growing rapidly. This has also raised higher requirements for production equipment: machines must be flexible, efficient, and easy to operate. One type of PVC window and door profile extrusion machine is now attracting a lot of attention in the market because it can produce different profiles simply by changing the mold.
One Machine, Many Products
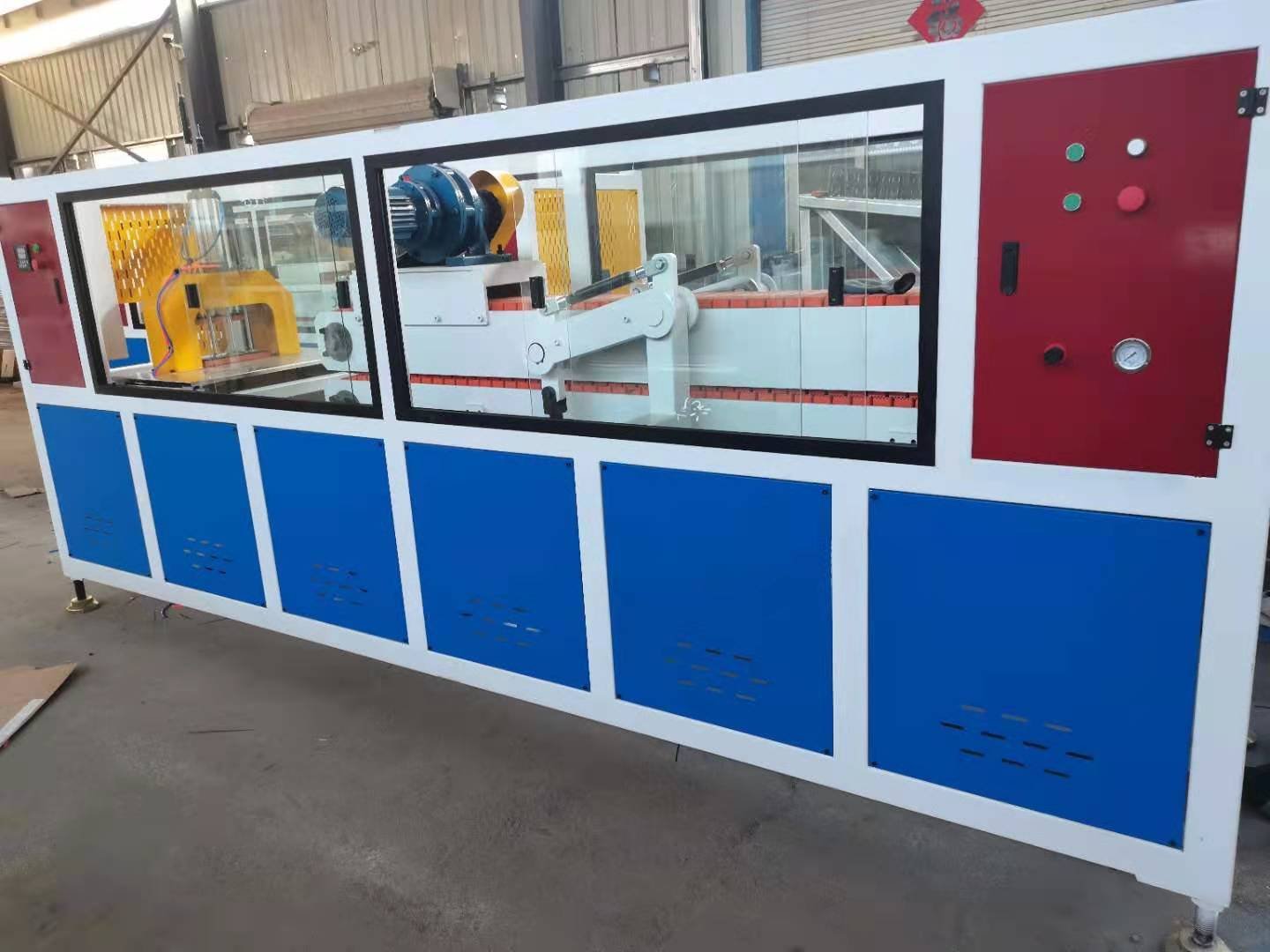
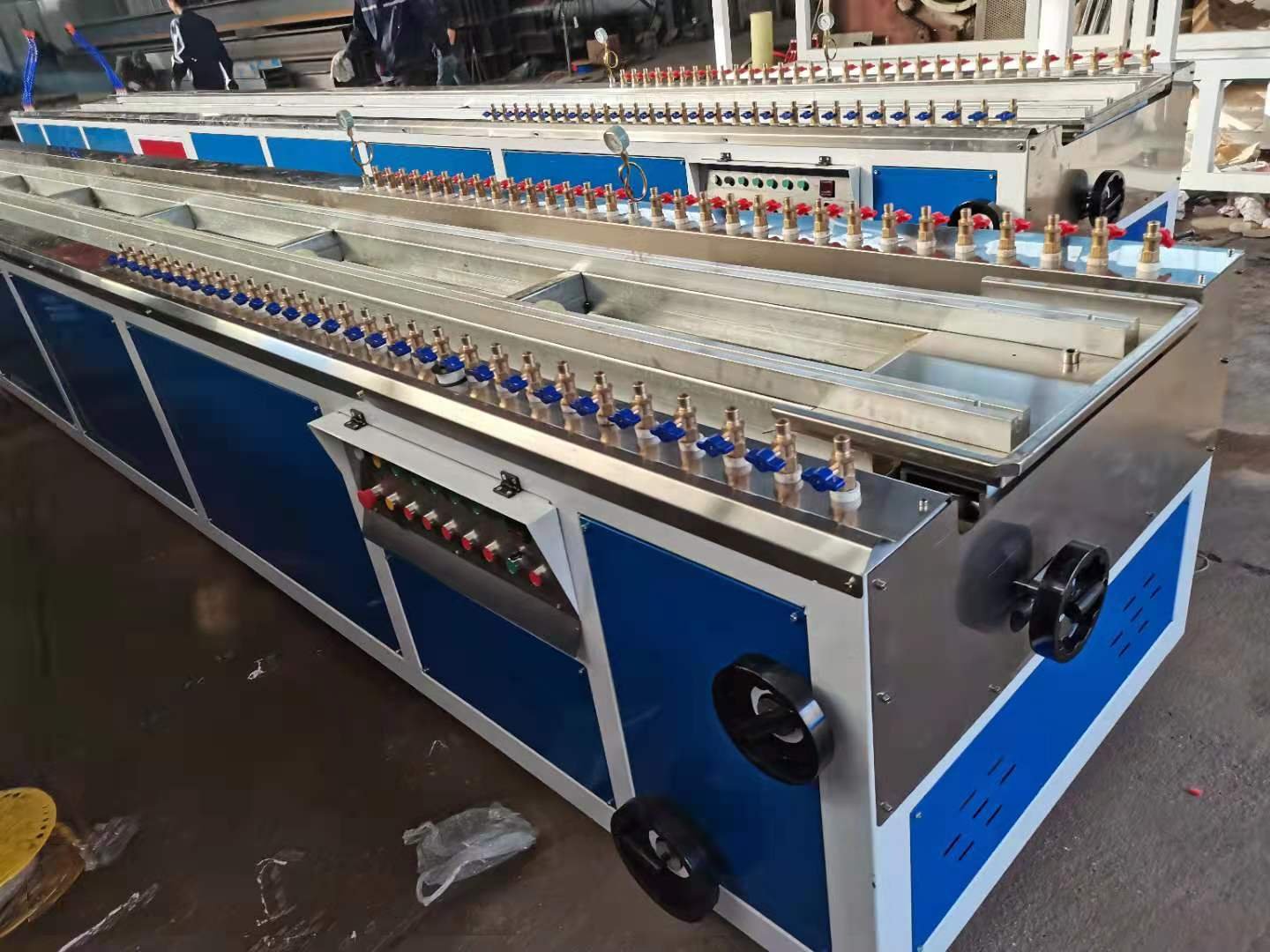
Traditional machines are often limited to making only one type of profile. In contrast, this advanced extrusion machine can easily switch molds to produce window frames, mullions, sashes, double and triple-pressure profiles, connectors, and corner profiles. This “one machine, many uses” feature helps manufacturers quickly respond to changing market needs and make full use of their investment.
Easy to Operate, Simple to Maintain
For many factories, ease of use is very important. The machine is designed with a smart control system and a clear, simple interface, so even new operators can learn quickly. Thanks to its modular design, maintenance is also easy, which means less downtime and lower costs.
Stable Performance, Reliable Quality
Stability is the key to high-quality products. This extrusion machine runs smoothly, ensuring the profiles have a clean surface, accurate dimensions, and consistent quality. At the same time, its energy-saving motor and heating system help reduce power consumption, which lowers operating costs.
A Smart Choice for the Future
Experts believe the future of the window and door industry will focus more on energy efficiency, eco-friendly production, and customized designs. A machine that can produce multiple types of profiles while maintaining high quality gives manufacturers a strong competitive advantage.
From single-function to multi-purpose, from complex operation to easy control, this PVC profile extrusion machine is helping many companies improve efficiency and prepare for long-term growth.